Parameterized Filters¶
Note
The algorithm for parameterized filters here was originally developed by Brett Morris for the tynt package.
Filter responses can be approximated using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). If a filter is approximated this way, one only needs to store its FFT parameters instead of all the sampled data points. This reduces the storage size and increases performance, at the cost of reduced accuracy. If you decide to use the parameterization functions provided here, it is up to you to decide whether the results are good enough for your use cases or not.
Generating FFT¶
You could parameterize a given filter using
filter_to_fft() as follows.
By default, 10 FFT parameters are returned as complex numbers:
>>> from synphot import SpectralElement
>>> from synphot.filter_parameterization import filter_to_fft
>>> filename = 'hst_acs_hrc_f555w.fits'
>>> bp = SpectralElement.from_file(filename)
>>> n_lambda, lambda_0, delta_lambda, tr_max, fft_pars = filter_to_fft(bp)
>>> n_lambda # Number of elements in wavelengths
10000
>>> lambda_0 # Starting value of wavelengths
<Quantity 3479.999 Angstrom>
>>> delta_lambda # Median wavelength separation
<Quantity 0.66748047 Angstrom>
>>> tr_max # Peak value of throughput
<Quantity 0.241445>
>>> fft_pars # FFT parameters
[(407.5180314841658+7.494005416219807e-16j),
(-78.52240189503877-376.53990235136575j),
(-294.86589196496584+127.25464850352665j),
(130.20273803287864+190.84263652863257j),
(96.62299079012317-91.70087676328245j),
(-32.572468348727654-34.227696019221035j),
(-8.051741476066471-21.354793540998294j),
(-51.708676896903725+6.883836090870033j),
(13.08719675518801+54.48177212720124j),
(38.635087381362396-13.02803811279449j)]
It is up to you to decide how to store this data, though storing it in a
table format is recommended. In fact, if you have many filters to parameterize,
filters_to_fft_table()
will store the results in a table for you:
>>> from synphot.filter_parameterization import filters_to_fft_table
>>> mapping = {'HST/ACS/HRC/F555W': (bp, None)}
>>> filter_pars_table = filters_to_fft_table(mapping)
>>> filter_pars_table
<Table length=1>
filter n_lambda ... fft_9
...
str17 int... ... complex128
----------------- -------- ... ---------------------------------------
HST/ACS/HRC/F555W 10000 ... (38.635087381362396-13.02803811279449j)
>>> filter_pars_table.write('my_filter_pars.fits')
Reconstructing Filter from FFT¶
Once you have a parameterized filter (see Generating FFT),
you can reconstruct it for use using
filter_from_fft().
Following from the example above:
>>> from synphot.filter_parameterization import filter_from_fft
>>> reconstructed_bp = filter_from_fft(
... n_lambda, lambda_0, delta_lambda, tr_max, fft_pars)
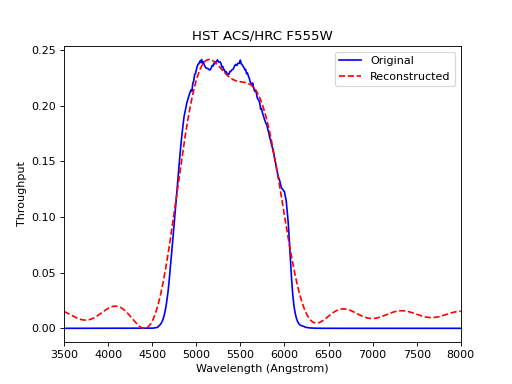
For this particular example using HST ACS/HRC F555W filter, perhaps 10 parameters are not quite sufficient. Therefore, caution needs to be exercised if you opt to parameterize your filters using this method.
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)